construction system
For the construction of wooden buildings and houses we rely on different construction systems, able to guarantee construction time significantly shorter than traditional systems, high levels of anti-seismic safety and high parameters of building durability.
Xlam and Telaio (platform) are construction types that have solidity and adaptability of wood as their minimum common denominator. But, at the same time, satisfy different needs such as high versatility and the need to create multi-storey wooden buildings.
Depending on the needs of each customer, our techinical team identifies the ideal construction system, illustrating and motivating this design choice thanks to the direct relationship between designer and client.
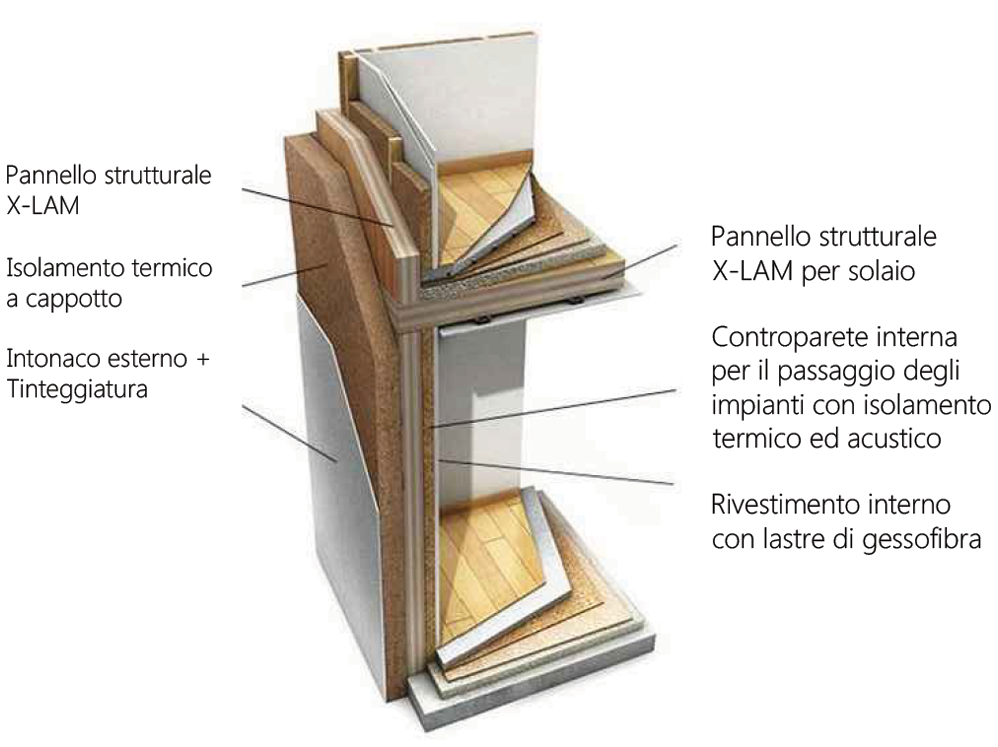
X-LAM
The X-Lam system represents technological innovation in the field of construction of wooden houses and buildings. The high versatility of this system allows for unusual architectural design, even for multi-storey wooden buildings. It allows excellent thermal insulation and guarantees high fire resistante, a fast drying process and good acoustic insulation.What is the Xlam system?
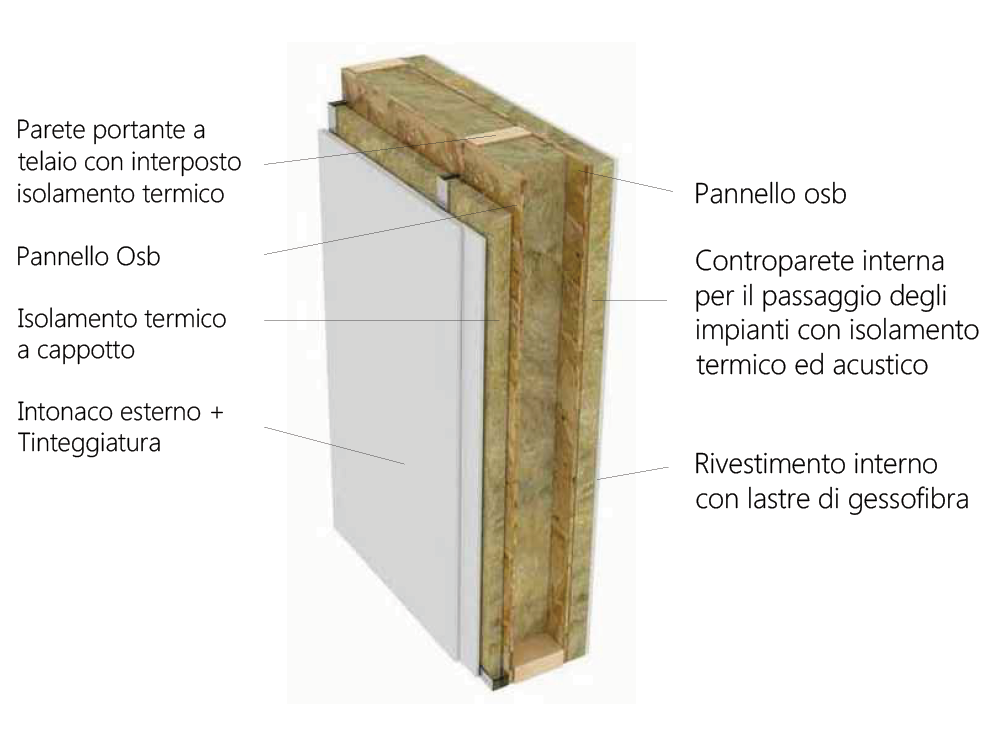
TELAIO
Telaio construction system uses columns (vertical) and beams (horizontal) in laminated wood to form the load-bearing framework of the building. These elements are arranged in such a way as to guarantee total flexibility in the design of facades and internal dividing walls. The strengths of this construction technology are: freedom of distribution of the walls in plan and possibility of moving them subsequently, architectural flexibility in the design of the facades and low incidence of cubic meters of timber per square meter built.
The diagonal bracings, made of wood or steel, or alternatively the beam-pillar nodes designed as joints or semi-joints, cover the functions of stiffering and bracing in response to seismic actions.

